Introduction
Sodium metabisulfite is an important chemical in leather manufacturing. It is widely used as a reducing agent and pH controller during hide preparation and tanning. Tanneries depend on sodium metabisulfite because it works in a controlled way, improves leather quality, and helps meet environmental rules. Its stable performance makes it a trusted material for both small and large leather producers.
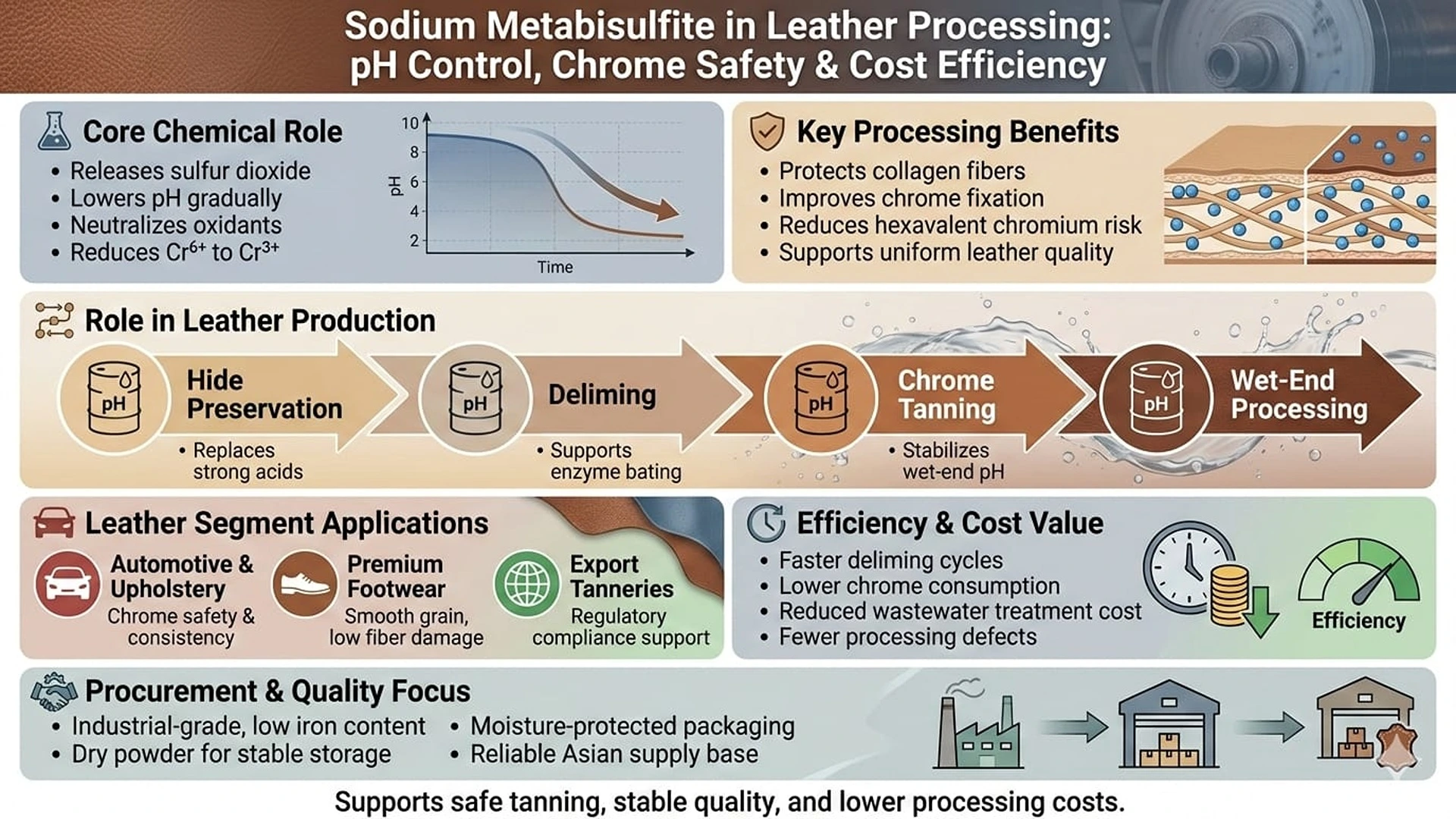
Chemical Role in Leather Manufacturing
Sodium metabisulfite works mainly by releasing sulfur dioxide when mixed with water. This reaction helps lower pH levels and remove unwanted oxidizing substances. In leather processing, this function is critical after alkaline soaking and liming stages, where the pH is very high.
During deliming, sodium metabisulfite reduces the pH to a level suitable for chrome tanning. This controlled pH drop allows chromium to bind better with the hide fibers. It also lowers the risk of forming harmful hexavalent chromium, which is tightly regulated in global leather markets.
Another key benefit is hide preservation. Sodium metabisulfite slows bacterial growth during raw hide storage and transport. This is especially useful in warm and humid regions, where hides can spoil quickly. Compared with salt-only preservation, it helps reduce weight loss and surface damage.
Because it lowers pH gently, sodium metabisulfite causes less fiber damage than strong mineral acids. This makes it suitable for high-quality leather, such as automotive upholstery and premium footwear.
Use Across Leather Production Stages
Sodium metabisulfite is used at several points in leather processing. In early stages, it helps preserve fresh hides before full processing begins. Tanneries apply it to reduce bacterial activity and maintain hide quality until further treatment.
During deliming, sodium metabisulfite replaces or reduces the use of ammonium-based chemicals. It creates a more even pH throughout the hide, which improves enzyme action during bating. This results in better fiber opening and a smoother final leather surface.
In chrome tanning, sodium metabisulfite plays a key role in reducing any remaining hexavalent chromium into its safer trivalent form. This improves chrome fixation, reduces chrome loss in wastewater, and supports compliance with environmental standards. It also helps stabilize pH during later wet-end steps such as neutralizing, retanning, and fatliquoring.
Dry powder form is commonly preferred by tanneries, especially in humid regions, because it is easier to store and less likely to release sulfur dioxide too early.
Differences Compared with Other Industries
Sodium metabisulfite is used in many industries, but its role in leather is unique. In textiles, it is mainly used to remove excess dye and protect fibers during bleaching. In pulp and paper, it neutralizes leftover chlorine to protect cellulose fibers.
In leather processing, the main focus is pH control, chromium reduction, and hide protection. Tanneries usually use industrial-grade material, which offers the right balance between cost and performance. Purity and low iron content are important to avoid staining or color issues on finished leather.
As sustainability requirements grow, sodium metabisulfite is also used in chrome recovery systems. These systems reduce chromium levels in wastewater and help tanneries meet stricter discharge rules in export markets.
Operational Benefits and Cost Control
Sodium metabisulfite helps improve production efficiency. Deliming times are shorter compared with acid-based systems, allowing faster processing and higher output. Its good solubility allows accurate dosing, which improves consistency and reduces waste.
Using sodium metabisulfite can also lower chrome consumption by improving chrome uptake. This reduces raw material costs and lowers treatment costs for wastewater. Its stable storage properties reduce losses during handling, as long as proper ventilation is used to manage sulfur dioxide gas.
From a cost perspective, sodium metabisulfite offers good value due to its multi-purpose use. One chemical can support preservation, deliming, chrome control, and wet-end stability. This helps simplify chemical inventories and lowers total operating costs.
Procurement and Quality Considerations
When sourcing sodium metabisulfite for leather use, buyers focus on consistent quality rather than food-grade purity. Key factors include reliable sulfur dioxide release, low heavy metal content, and good solubility.
Suppliers usually ship the product in sealed bags or bulk containers to protect it from moisture. Proper storage in cool, dry conditions helps maintain performance for up to one year. Quality testing, such as assay checks and sulfur dioxide measurements, ensures each batch meets process needs.
Stable supply from major Asian producers supports long-term procurement planning, especially for tanneries supplying export markets with strict compliance requirements.
Conclusion
Sodium metabisulfite is a vital chemical in modern leather processing. Its ability to control pH, protect hides, improve chrome tanning, and support environmental compliance makes it highly valuable across the production chain. When used correctly, it improves leather quality, reduces processing time, and lowers overall costs. As regulations around chromium and wastewater become stricter, sodium metabisulfite will continue to play a key role in efficient and sustainable leather manufacturing.
Leave a Comment